IPTV Tutorial: What Is IPTV (Internet Protocol Television)? Terrestrial broadcast system formats (cable and satellite) are used in the traditional dissemination of television programmes. However, Internet Protocol TV, or IPTV, uses Internet Protocol (IP) networks to provide television series transmission via the Internet.
Due to its features, which let users watch films, TV series on their preferred channels, live sporting events (like football or cricket), and even past episodes of their favourite shows, Internet Protocol TV has become the most popular television service.
What is IPTV?
Broadband media that distributes multimedia services—such as television, audio, video, graphics, and so on—over Internet protocol networks to ensure the content’s desired quality, security, and dependability is known as Internet protocol television.
The most effective way to transmit television shows is now via IPTV. It often operates on a request basis, broadcasting just the content that the user requests. Every time you change your channel, the viewer will get a fresh batch of streams.
Conversely, all the channels are aired concurrently in the traditional TV programme broadcasting style.
As a result, these days, if you have a broadband connection, you can view it on a PC, laptop, or smartphone.
YOU MAY LIKE ⇒ IPTV UK FREE TRIAL
Types of Internet Protocol Television
#1) Live Television: This refers to live television broadcasting or live streaming of films, music, games, and other content with the least amount of delay, such as viewing a live football game, cricket match, or reality game show finale in real-time as it is occurring.
#2) Digital Video Recorder (DVR) or Time-shifted Television: This allows you to see replays of currently airing programming and ones originally aired many hours or days ago.
Users have the option to watch their preferred TV programmes at a later time, even if they are unable to see them live due to scheduling conflicts.
#3) Video on Demand (VOD): Every user will have a variety of media files saved on their device, which they may explore and view whenever they like. This Internet Protocol TV feature employs a unicast transmission method using the real-time streaming protocol.
These days, Entertainment Netflix and Amazon Prime Video are the two most demanding VoD providers.
A Few Internet TV Features
- This technology offers interactive television that is capable of going in both directions. As a result, it allows subscribers to customise their experience by selecting what and when to watch content.
- Service providers may save bandwidth since the material is only broadcast in response to end users’ requests inside the network.
- In addition to TV, we may watch the services on computers, laptops, tablets, and cellphones, among other devices.
- In addition, it has capabilities like a multimedia player, weather information, fast-forwarding TV (which skips commercials), and stopping.
- TV, replaying TV, and listening to music on demand.
- Since many of the videos we view online feature ad insertion, which prevents us from skipping any of them, advertising is also possible via IPTV.
IPTV’s Past
- The Windows and UNIX-based applications compatible with Mbone used the real-time transport protocol (RTP) and real-time control protocol (RTCP) to transmit audio and video content from one or more sources.
- Kingston Communications, a UK-based telecom company, introduced IPTV using a digital subscriber line (DSL) in 1999.
- One of the American companies introduced the Internet Protocol TV high-definition channel in 2005.
- In addition, several Asian and European nations started offering video-on-demand (VOD) services in 2010 in conjunction with IPTV providers. They also introduced set-top boxes with DVR services.
Market Capacity
- According to estimates, there are already over a billion users worldwide, with the number predicted to rise to over a billion by 2025, with the United States and Europe leading the way.
- Globally, IPTV service demand rises between 30 and 35 per cent annually.
- The primary driver of IPTV’s market expansion is the enormous desire for personalised TV programming. One of the main things that helps this industry grow faster and provide more marketing and income is the addition of on-demand advertising alongside the content.
- According to the report, Asia-Pacific nations, including China, South Korea, and India, are growing IPTV markets based on North American and European market patterns.
- European nations, including France, Germany, and the United Kingdom, have the most market shares of all the IPTV.
- Are some of the major IPTV providers offering services in the worldwide market?
- Thanks to the rapid expansion of high-speed broadband Internet services nationwide, India is now the Internet Protocol TV market with the fastest growth rate. Due to this expansion, the Internet Protocol TV industry is worth more than $100 million in revenue.
- In 2015, Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited introduced 4G services in India that provide voice over LTE and other internet services. In 2016, JIOTV, a service that offers live TV, cricket, DVR, and other content, was introduced.
- Together with JIOTV, Reliance JIO has introduced several other services. JIO CINEMA allows users to watch the newest films and web series on demand. JIO Saavan will enable users to listen to music offline and online in various languages.
Architecture Of IPTV
IPTV’s architecture’s four primary building components are:
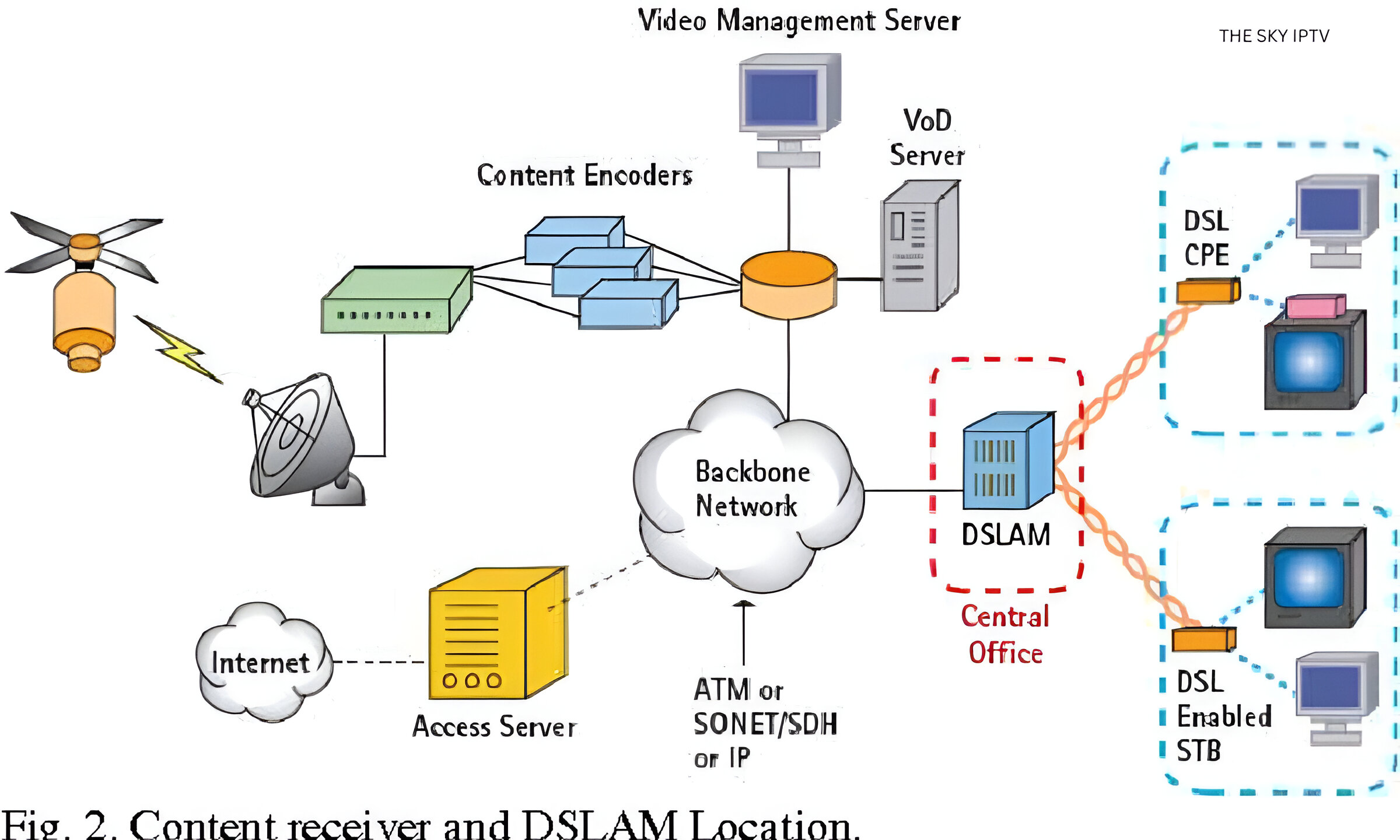
- The subscriber’s house.
- The local end office.
- The video serves the office.
- The super head-end.
The Role Of The Super-head End
Every programme that airs daily on the national TV channels will be downloaded and stored by the superhead end wing.
Afterwards, the programme material is altered to be sent across fast internet connections, such as DSL and FTTH networks. The various multicast IP addresses are used for IPTV channel delivery.
Using the multi-program transport stream to the video or data nodes of the far end, the super-head end will float the material to the local office ends. In addition to obtaining the video from several sources, the head end delivers the data content via a media streamer and MPEG encoder.
The head end uses digital rights management (DRM) and conditional access (CAS) systems to provide content security.
The Function Of Video For Office Use
This will include and store the advertising server, video on demand, and local content. In addition, it can broadcast material over high-speed IP lines to the zonal end offices and a wireless antenna.
The function of the local office ends
The digital subscriber line access multiplexer, or DSLAM, is the primary component at the local end offices. Its primary function is to combine IP video services, data, and phone services.
Currently, the primary duty of the local end office is to aggregate all of this data and provide it over STM or digital subscriber line (DSL) lines to the user’s local region. The DSL will also function as a splitter because it modifies the material’s format so the end user can access and need it.
The End of the Subscriber
The DSL modem transforms IP data into a format suitable for a laptop or desktop computer if the end user requests content in a data format. The STB (set-top box), which enables it to be used on a TV, extracts the video material.
Two architectural types are recommended to maximise the bandwidth allocated to the video server networks, which will need enormous bandwidths to store and broadcast the stored and on-demand media.
Models of Architecture
- One viable approach for distributing short web series and tiny VOD materials is the centralised architecture model, which stores all content on a single centralised server.
- The other is a distributed architectural model, in which different nodes within a network get various amounts of bandwidth based on the needs of the network, and content is dispersed among them.
Although the distributed design is a little complicated, it works well for delivering a lot of material over huge networks that major service providers use.
Minimum Bandwidth Needed
For SDTV, the required IPTV bandwidth for the access link is 4 MBPS per channel, and for HDTV, it is 20 MBPS per channel. A high-definition video quality requires a bandwidth requirement of 25 MBPS for video-on-demand.
Set-top box for IPTV (STB)
- The STB’s job is to transform the incoming, acceptable signal into a video signal that users can view on their TVs by using an HDMI, AV, or, more frequently these days, wi-fi connection.
- The STB has two ends: one connected to the TV and the other to the internet using a router or modem and an RJ45 connector cable that provides high-speed internet access to residential spaces.
- The set-top box includes many more ports and features, but we will only cover some because they are unimportant.
- Connecting the set-top box to a tablet or smartphone using LTE wi-fi networks is simple.
The Internet Protocol and TV Protocols
IPTV offers live TV, a multicast service, and video on demand (VoD), a unicast service. The broadband fixed or wireless IP network is connected to embedded operating system devices such as tablets, smartphones, game consoles, PCs, and set-top boxes.
The MPEG transport stream, or RTP packets, encapsulates archived VoD services. The H via telecast. 263 or H.264 codec is used for video compression, while the MDCT codec is used for audio compression.
Current procedures in use are listed below:
- The IGMP protocol is use for service provider-based video streaming. It can also be used to switch between different live-streaming channels.
- Protocol-independent multicast (PIM), which distributes TV channels from the source to the destination consumer end that wishes to view the content, handles the routing in the network.
- A real-time transport protocol (RTP) via UDP is used to watch on-demand material. The encapsulation technique used in this instance is the H.222 transport stream over TCP.
- RTP over TCP or UDP is utilised by deploying RTSP over TCP for setup and control in web-based unicast and multicast live streaming.
Mixture IPTV
The common satellite and cable TV operators should devise a solution to preserve their business by allowing consumers to watch Internet-based video and TV channels on television sets, given the growing demand for watching online video sites like YouTube.
In addition, the pay-TV providers want them to provide the necessary service without putting further strain on their networks’ equipment or costs.
Hybrid IPTV is an excellent option for satisfying the needs of both pay-TV providers and subscribers. It combines video-on-demand based on IP networks with traditional broadcast TV services.
With no additional infrastructure, the television subscriber can now watch TV channels and video content from a larger selection of available content.
In addition, several cutting-edge services like TV show reruns, online gaming, shopping, online baseball, live game streaming, e-governance, and more may be accessed directly on the television screen using hybrid IPTV set-top boxes.
As TV operators, providers can allow users to access the services listed above based on their needs and requests to turn the service on or off. This gives the service provider and the end-user freedom without adding network or service complexity.
Benefits Of IPTV

- The IPTV service is incredibly cost-effective because we only need to install the set-top box to view the material.
- Obtaining its most recent versions using a wi-fi connection is also simple.It facilitates ease of use.
- Since Internet Protocol TV is entirely digital, it can support the newest technological innovations, ensuring a high quality of service.
- Viewing multiple shows simultaneously on smartphones and TV screens without disruptions is possible.
- We can employ voice, data, online gaming, real-time batting, telephone, and video-on-demand services.
- By forwarding the advertising from the remote, viewers can avoid the commercial breaks between TV shows and other programming.
- Because the end user may watch shows from the stored server whenever they want and can pause and play the content according to their preferences by utilising the fast-forward, rewind, and pause buttons, the IPTV system is user-friendly and time-efficient.
Internet Protocol TV’s Restrictions
There is no assurance that watching IPTV broadcasts will be error-free. For example, the server will get busy if multiple users watch the same show simultaneously. This makes it impossible for the end user to watch the video and causes the channel to display an error.
Certain channels occasionally delay after every 30 seconds of playback and take a very long time to start a show. If this occurs frequently, consumers will lose interest in viewing the show.
It frequently hangs due to synchronisation issues between the video-serving office and the end user.
Conclusion
This course covered several topics related to IPTV, one of the newest developments in the communication and entertainment sectors.
We also looked at the IPTV’s architecture, how its multiple components function together, its benefits, and its drawbacks.

Leave a Reply